Massive Phishing Attack: Hackers Targeted 130+ Companies
Over 130 organizations, including Twilio, DoorDash, and Cloudflare, have been compromised by hackers as part of a months-long phishing campaign,security researchers call “0ktapus.”

According to a report from cybersecurityGroup-IB, login credentials belonging to nearly 10,000 individuals were stolen by attackers who imitated the popular single sign-on service Okta.
Attackers then used that access to pivot and attack accounts across other services.
On August 15th, attackers breached Twilio, which handles text messaging for phone number verifications, and were able to register new devices to the accounts of Signal users without having access to Signal directly.
Signal alerted 1,900 users that their accounts were potentially revealed to whoever hacked Twilio and said that the attackers searched for three specific numbers during the time they had access.
Signal confirmed attackers were able to register new devices to a few of the accounts, which would allow the criminals to send and receive from that account.
Twilio also updated its breach notification, noting that 163 customers had their data accessed. 93 users of Authy,Twilio’s cloud service for multi-factor authentication, also had their accounts accessed and additional devices registered.
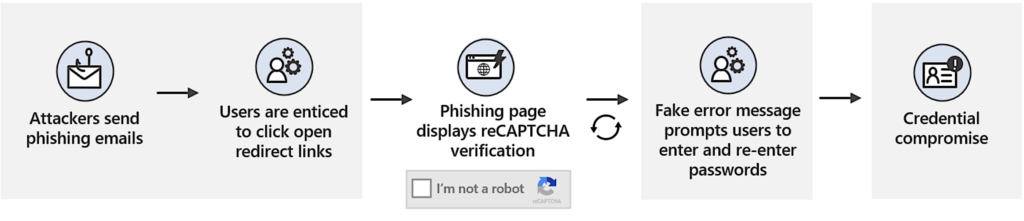
Targets of the phishing campaign were sent text messages that redirected them to a phishing site, which from the victim’s point of view, looks quite convincing, as it is very similar to the authentication page they are used to seeing.
Victims were asked for their username, password, and multi-factor authentication code. This information was then sent to the attackers.
Interestingly, Group-IB’s analysis suggests that the attackers were somewhat inexperienced. The phishing kit revealed showed it was poorly configured and provided an ability to extract stolen credentials for further analysis.
However, inexperienced or not, the scale of the attack is massive, with Group-IB detecting 169 unique domains targeted by the campaign.
It’s believed that the 0ktapus campaign began around March 2022 and that so far, around 9,931 login credentials have been stolen.
The attackers have spread their net wide, targeting multiple industries, including finance, gaming, and telecoms.
Domains cited by Group-IB as targets (but not confirmed breaches) include Microsoft, Twitter, AT&T, Verizon Wireless, Coinbase, Best Buy, T-Mobile, Riot Games, and Epic Games.
At least one of the motives for the attacks is stealing money, with seeing financial companies in the compromised list.
Furthermore, some of the targeted companies provide access to crypto assets and markets, whereas others develop investment tools. Group-IB warns that we likely won’t know the full scale of this attack for some time.
In order to guard against similar attacks like this, always be sure to check the URL of any site where you’re entering login details and treat URLs received from unknown sources with suspicion.
For added protection, you can use an “unphishable” multi-factor security key, such as a YubiKey.
This recent string of phishing attacks is one of the most impressive campaigns of this scale to date.
Oktapus shows how vulnerable modern organizations are to some basic social engineering attacks and how far-reaching the effects of such incidents can be for their partners and customers.
The scale of these threats isn’t likely to decrease any time soon, either. Research from Zscaler shows that phishing attacks increased by 29% globally in 2021 compared to 2020.
SMS phishing in particular is increasing faster than other kinds of scams as people have started to better recognize fraudulent emails.
The APWG’s Phishing Activity Trends Report reveals that in the first quarter of 2022 there were 1,025,968 total phishing attacks, the worst quarter for phishing observed to date.
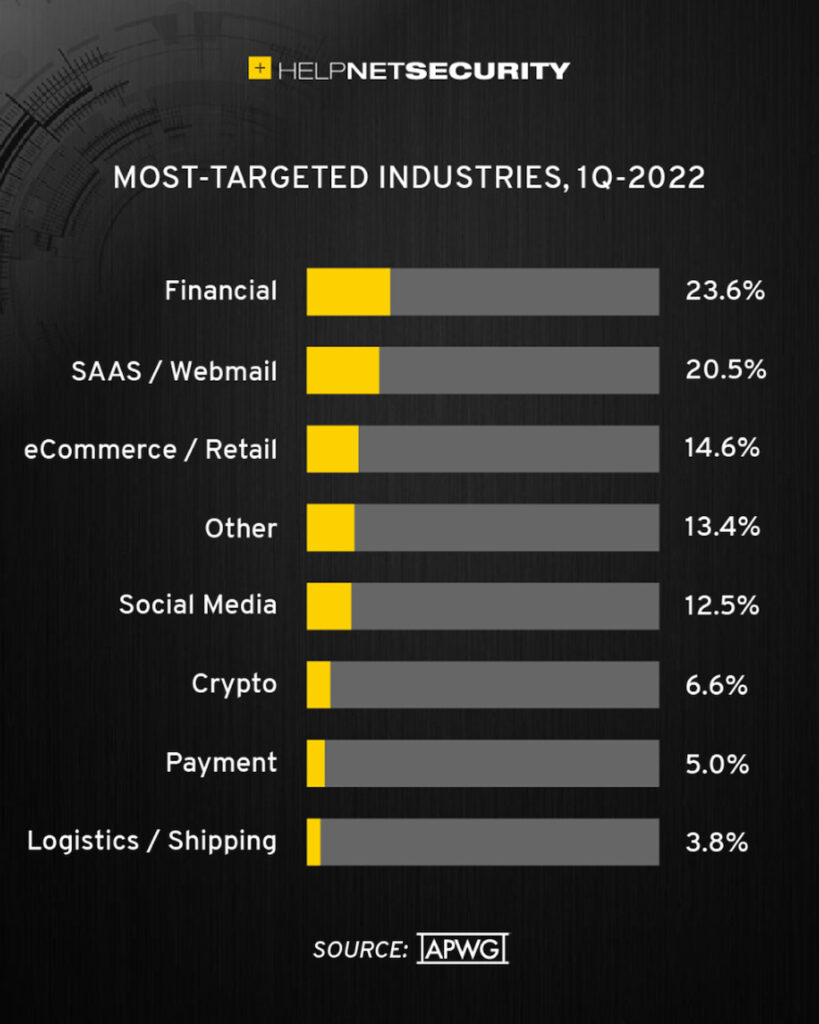
Socially engineered scams and hacks were also seen rising during the COVID-19 pandemic, and earlier this year, we even saw that both Apple and Meta shared data with hackers pretending to be law enforcement officials.
Depending on the scope of the attack, phishing could escalate into a security incident from which a business will have a very tough time recovering from.
With a better understanding of the types of phishing attacks and how to identify them, individuals and organizations can better protect themselves from falling victim.








