Email Security 2023: 4 Must-See Trends In The Industry
Keeping up with the latest developments in email security is critical for your business cyber defences.

In H1 2022, Vade detected more than 440 million phishing and malware-laced emails, a figure illustrating that cybercriminals remain as active and motivated as ever.
Fortunately, organizations can take steps to stay ahead of the curve, such as becoming more cyber-aware, securing networks, and updating technology to prevent or minimize the potential damage caused by attacks.
Tips To Strengthen Your Business Cyber Security Posture
Below are some of the annual email security predictions by experts at Vade, who share their insights on the biggest threats and developments that will shape email security in 2023.
1. Phishing Attacks Will Target MFA & Legitimate Services
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is no longer a novel concept for organizations, but a widely used security measure that uses at least two different login methods to verify a person’s identity.
While MFA is an important cybersecurity solution, hackers have developed techniques to bypass it. This enables them to exploit organizations’ overconfidence in the security of the tool, which they often see as a silver bullet.
According to Romain Basset, Director of Customer Services at Vade, “We’ll see more phishing campaigns that are able to circumvent MFA by acting as a proxy with the real authentication system, or by tricking users who have MFA fatigue.”
Basset points to a recent case in September 2022, when MFA fatigue enabled a hacker to compromise Uber’s internal networks.
Basset predicts an increase in phishing campaigns that abuse legitimate services to distribute phishing links.
“Recent attacks on a top career service in France is a great example of a legitimate platform being weaponized,” he says. In the attack, hackers applied to job postings and used the platform’s legitimate infrastructure to transmit phishing links to companies recruiting candidates. Vade first detected the phishing scam in September 2022.
While new phishing scams are emerging, the Cyber Threat Experts (CTE) Team at Vade says organizations should also remain cautious of time-tested scams.
“Tax-themed phishing campaigns, payment scams, and delivery schemes are still effective, relevant, and common. Attackers will continue to deploy them, while improving the content and techniques of their attacks. They test email filtering components daily to find weaknesses and bypass them to deliver their campaigns.”
Recent Phishing Scam Examples & Helpful Resources:
- How To Prevent Online Marketplace Fraud: 6 Scam Examples – https://www.bvainc.com/2022/12/13/how-to-prevent-online-marketplace-fraud-6-scam-examples/
- Massive Phishing Attack: Hackers Targeted 130+ Companies – https://www.bvainc.com/2022/09/01/massive-phishing-campaign-targeted-over-130-companies/
- New Cyber Scam Uses Fake Invoice Phishing Emails – https://www.bvainc.com/2022/11/29/new-cyber-scam-uses-fake-invoice-phishing-emails/
- The Most Common Online Fraud & Cyber Crime Terms – https://www.bvainc.com/2022/12/08/the-most-common-online-fraud-cyber-crime-terms/
2. Supply-Chain & Hijacking Techniques Will Increase
Organizations are investing more in phishing awareness training to strengthen the human element of their cyber defenses, which is their greatest vulnerability to a cyberattack.
While improved user awareness is welcome news, Michael Posey, Pre-Sales Engineer at Vade, believes it will force attackers to evolve their methods.
“As users become more proficient at spotting and reporting common phishing scams from well-known brands, we will see hackers adjust their strategy, including impersonating suppliers or customers. I expect more supply-chain attacks and hijacking,” he says.
Supply-chain attacks refer to cyberthreats that infiltrate an organization’s systems by impersonating or compromising vendors with access to those systems.
Hijacking, on the other hand, refers to attacks in which hackers use compromised accounts to join existing email communications or create new ones. Once hackers enter those conversations, they deploy phishing or spear-phishing attacks.
Still, Posey believes phishing campaigns impersonating established brands like Facebook and Microsoft will continue. Vade’s Phishers’ Favorites H1 2022 Report, which reveals the top brands impersonated by hackers, supports his prediction.
Top 10 impersonated brands in phishing in H1 2022, based on unique phishing URLs
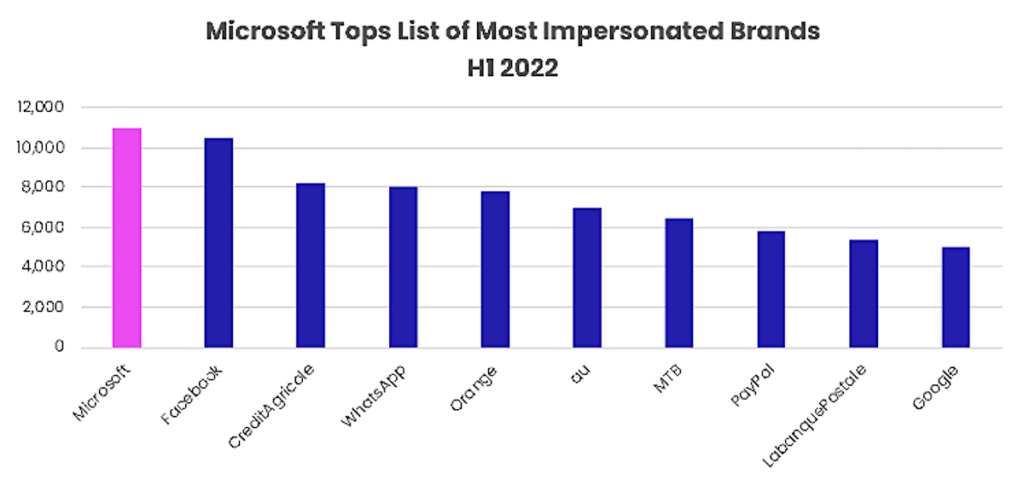
Microsoft emerged as the most impersonated brand in H1 2022, accounting for a total of 11,041 unique phishing URLs. Facebook took the second spot with 10,448 unique phishing links, while Crédit Agricole, WhatsApp, and Orange rounded out the top five on the list.
While phishing emails have long been used to victimize users indiscriminately, more recent campaigns reveal a more focused approach.
Cyber criminals are becoming more sophisticated with their methods, a recent Instagram phishing scheme showed hackers researched their victims before carrying out highly targeted attacks.
3. Ransomware Attacks Will Continue Their Devastation
Ransomware attacks have regularly made headlines in recent years, and the CTE Team predicts this devastating type of cyberthreat to continue to wreak havoc on organizations.
Similar to last year, we expect ransomware attacks to get more sophisticated in terms of evading detection, adapting, and exploiting new vulnerabilities to spread. Ransomware groups like BlackCat are fine-tuning their methods.
The two main factors maintaining the volume of ransomware attacks:
- Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS)
- Double Extortion
Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) is a key source of revenue for cybercriminals. Hackers will remain active as long as that’s the case. It also allows hackers who are less skilled to get their hands on sophisticated ransomware and turn a profit.
Double extortion gives hackers additional leverage over their victims. Data exfiltration and the threat of leaking sensitive data gives organizations more reason to comply with hackers’ demands to avoid regulatory, legal, or reputational consequences.
Consistent with other types of cyberthreats, the CTE Team believes hackers will continue to focus their ransomware attacks on smaller organizations.
“Already, we’re seeing attackers target small-to-midsized businesses (SMBs) rather than larger enterprises. SMBs lack the same cybersecurity resources and budgets, making it easier for hackers to exploit them.”
Today’s cyber criminals appear to be favoring the ease and efficiency of targeting smaller businesses over the larger payouts they may earn by attacking big enterprises.
4. Productivity Suite Security Will Supersede Email Security In 2023
Email is deeply integrated with an organization’s various internal systems, processes, departments, and more. Email security will need to be a top priority, by extending protection beyond users’ inboxes and outboxes.
As attacks grow in number and sophistication, SMBs will need technology that tightly integrates with modern productivity suites such as Microsoft 365 or Google Workspace and provides comprehensive threat intelligence.
Unlike secure email gateways (SEGs) that separate email security from internal networks, API-based alternatives are the future of email security.
Organizations need to be able to leverage the threat intelligence from email to protect file sharing applications and other collaborative tools like instant messaging.
SMBs also need to be able to leverage information such as user profiles, contacts, and communication patterns to defend against highly targeted attacks, such as those we’re seeing with supply-chain attacks.
According to the CTE Team, email gives hackers a clear advantage over their victims by disguising cybercriminals’ activities. “Hackers benefit from the sheer volume of emails sent every day, requiring organizations to triage vast amounts of data to detect threats.”
“Coupled with demands to keep their systems free from vulnerabilities and provide around-the-clock protection, organizations struggle to keep pace with hackers.”
The right technology and IT support will provide organizations with a strong and structured plan to overcome this disadvantage.
Here at BVA Technology Services, we provide organizations of all sizes and industries with IT solutions that can detect low volume threats affecting users or customers, and are able to quickly remediate them.
Strengthening Email Security For 2023 & Beyond
Cyber criminals continue to launch more targeted and creative attacks against their victims. Therefore, it’s necessary for organizations to invest more time and resources into cybersecurity and user awareness.
Expect hackers to further enhance their methods, through common attack methods such as:
- MFA Exploitation
- Hijacking
- Supply-Chain Attacks
- Double Extortion
- Business Email Compromise Attacks
- Social-Engineering Attacks
No matter their approach, email will remain the top vector for cyberthreats.
“The majority of attacks will continue to start with email, since it’s the most efficient and direct path to organization’s greatest IT vulnerability, and that is end users,” says the CTE Team.
To keep pace with hackers, organizations need AI-based threat detection and response technology to defend against known, emerging, and never-before-seen email-borne threats.
Importantly, organizations should look for solutions that live within their internal environments and provide protection against threats originating from compromised accounts or flowing freely through their productivity suites.
Phishing Awareness Training For Your End Users
It’s 2023 and Cyber Crime is still on the rise. Cyber criminals continue to relentlessly attack organizations, big and small, with more sophisticated emails, phishing, and social engineering tactics.
- 89% of phishing attacks orchestrated by professional cyber crime organizations.
- 66% of malware is now installed via malicious email attachments and advanced spear phishing techniques, costing business on average $140,000.
- 41% of IT Pros report AT LEAST DAILY phishing attacks.
- 30% of phishing emails are opened.
It’s essential that your business stay ahead of the curve, implementing a multi-layer security posture with physical controls, software controls, and end user training to prevent your easiest target from falling victim.
Here at BVA Technology Services we are partnered with Sophos to keep businesses and users safe and up to date. We highly recommend Sophos Phish Threat Service, it provides effective phishing simulations, automated training, and comprehensive reporting.
Sophos Phish Threat is a phishing attack simulation and training for your end users!
For just ($2.90/month) we’ll set you up with Sophos Phish Threat, so your organization can begin cultivating a positive security awareness culture through testing, training, and reporting.
How Phish Threat Works:
- On a reoccuring basis, Phish Threat sends out 1 of 500 realistic phishing attacks to your internal staff.
- Each email is tracked to see who opens the email, clicks on any links, and/or provides their credentials.
- Any users caught are automatically enrolled in an interactive training module that will educate the end user about the specific threat in that particular email.
- Users can report the suspected phishing email wtih the user of an outlook add-in.
- All actions are gathered in Sophos Central to provide comprehensive reporting on the users who have been caught, the number of times they have been caught, and if they have completed the training or not. This allows you to enforce accountability of those trainings.
What The Phishing User Training Covers:
- Current phishing, credential harvesting, and malicious attachment campaigns.
- Socially relevant attack simulation templates.
- Scheduled Monthly Training Campaigns.
- Covering multiple scenarios from beginner to expert.
While there’s no silver bullet when it comes to preventing all cyber security attacks, putting appropriate measures and training in place can significantly reduce the chances of it happening.








